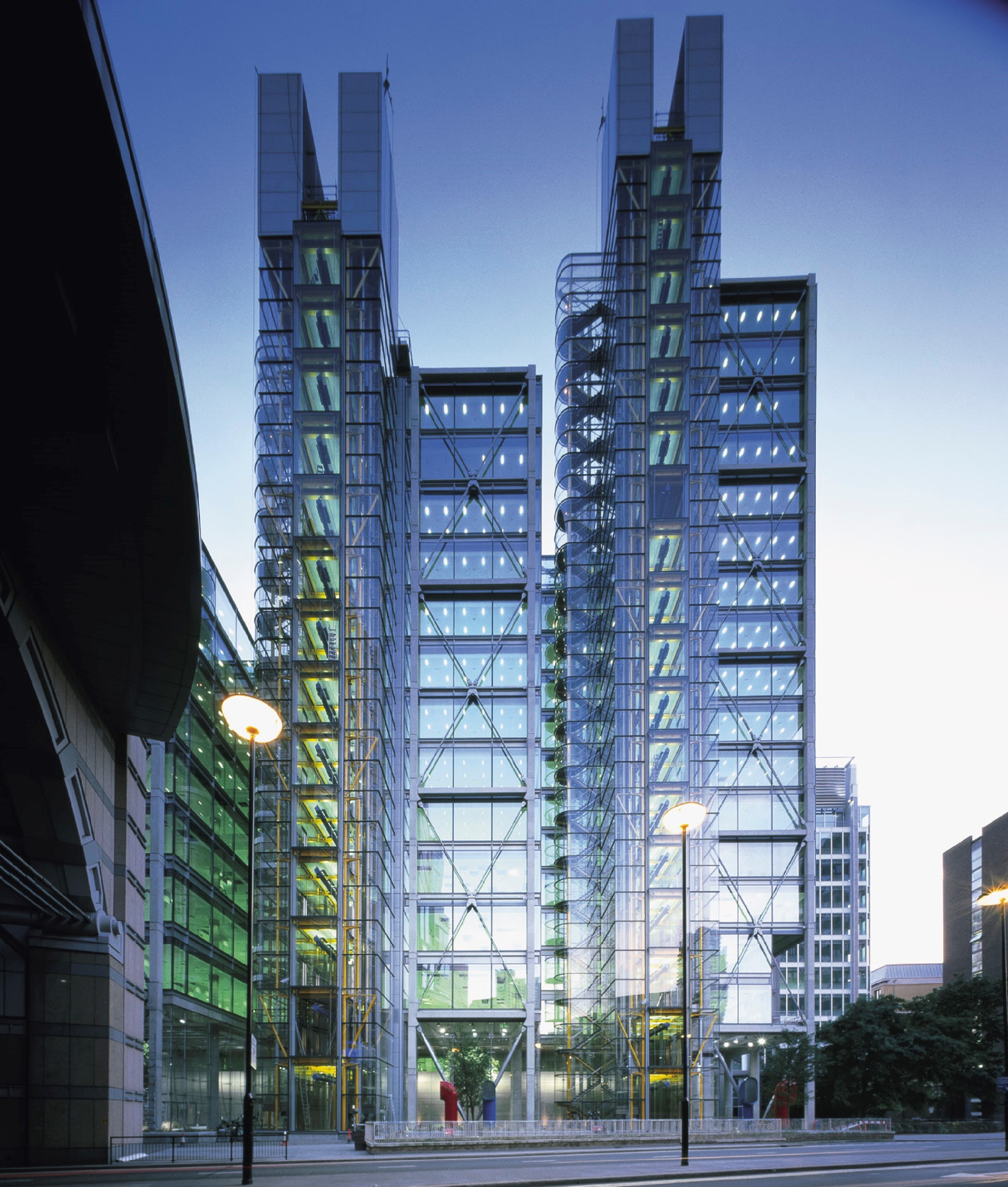
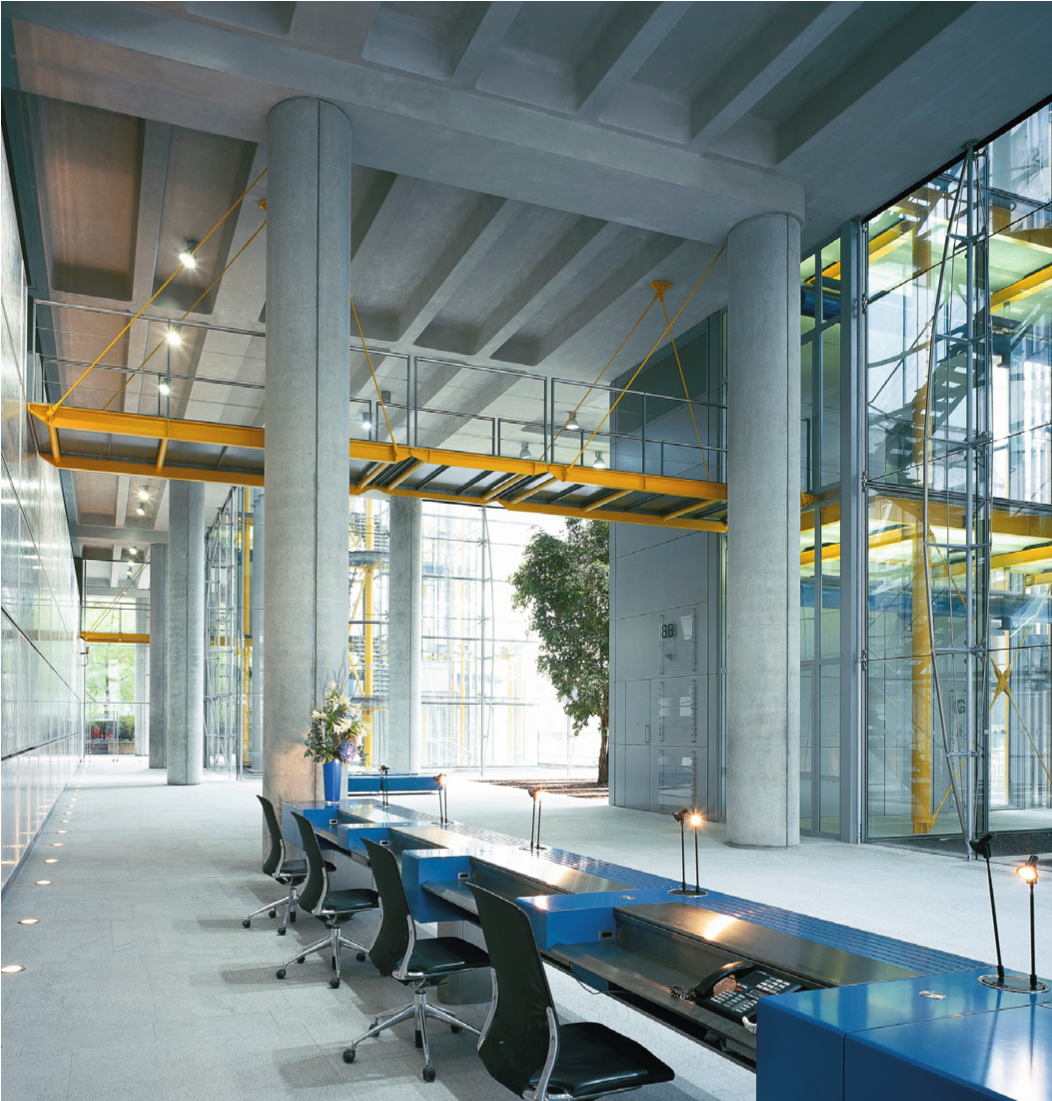
88 Wood Street
“With its unapologetic modern facade, the building combines a jagged profile in an elegant concrete frame ... oozing an airy spirit full of honesty but not lacking in bravado.” Don Barker, Architecture Week
88 Wood Street demonstrates the potential for speculative commercial development that does not compromise on quality and enhances the public domain.
The site was formerly occupied by a 1920s telephone exchange – delays in securing the demolition of this building, combined with the onset of an economic recession in the 1990s, led to the cancellation of a scheme for a prestige banking headquarters. A larger scheme was designed in 1993–94, with speculative letting in mind.
This building is arranged as three linked blocks of office accommodation that step up from eight storeys on Wood Street, where the context includes two listed buildings, to 14 and finally 18 storeys to the west, responding to the taller built topography towards London Wall. The connections between blocks provides a very large floor area that can be easily subdivided. By using the extensive basement of the telephone exchange for the building plant, roof levels are kept largely free.
The office wings are constructed of in-situ concrete, contrasting with the lightweight, steel-framed service towers. The use of brilliant colour enhances their impact – air intakes and extracts at street level are also brightly coloured, contrasting with the neutrality of the occupied floors. The façades of the main office floors are glazed from floor to ceiling to maximise daylight and views – in addition, levels 8,12 and 16 lead directly onto roof terraces with spectacular views over the City.
Though built to a strict commercial budget, 88 Wood Street contains many innovative elements. Its triple-glazed façade is formed of single panels of highly transparent float glass. The inner faces of the external panes have a low emissivity coating which further reduces solar gain, while the cavity between the double glazed units and the third panel is fitted with motorised, integral horizontal blinds with perforated slats. Photocells on the roof monitor light conditions and adjust the angle of the blinds, thus minimising glare, heat gain and energy consumption.
Project information:
- Place: London, UK
- Date: 1993—1999
- Client: Daiwa Europe Properties
- Cost: £52 million
- Area: 33,073m²
- Structural Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners
- Services Engineer: Ove Arup & Partners
- Quantity Surveyor: Gardiner & Theobald
- Project Manager: D J Williams & Associates Ltd
- Construction Manager: Laing Management Ltd
- Main Contractor: Kajima/Laing Management Joint Venture
- Fit-Out Contractor: Kajima/Hazama Joint Venture
- Landscape Architect: Edward Hutchison
Awards:
2002
- The American Institute of Architects London/UK Chapter
- Excellence in Design Award Winner
2000
- RIBA Award/Stirling Shortlist
- Civic Trust Award
- Royal Fine Art Commission Trust Award
- Royal Academy Summer Exhibition Bovis/Lend Lease
- Award for Best Architectural Exhibit
Click here to see the full job sheet.
--RSHP
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Classroom electrician courses a 'waste of money'
Say experts from the Electrical Contractors’ Association.
Wellbeing in Buildings TG 10/2025
BSRIA topic guide updates.
With brief background and WELL v2™.
From studies, to books to a new project, with founder Emma Walshaw.
Types of drawings for building design
Still one of the most popular articles the A-Z of drawings.
Who, or What Does the Building Safety Act Apply To?
From compliance to competence in brief.
The remarkable story of a Highland architect.
Commissioning Responsibilities Framework BG 88/2025
BSRIA guidance on establishing clear roles and responsibilities for commissioning tasks.
An architectural movement to love or hate.
Don’t take British stone for granted
It won’t survive on supplying the heritage sector alone.
The Constructing Excellence Value Toolkit
Driving value-based decision making in construction.
Meet CIOB event in Northern Ireland
Inspiring the next generation of construction talent.
Reasons for using MVHR systems
6 reasons for a whole-house approach to ventilation.
Supplementary Planning Documents, a reminder
As used by the City of London to introduce a Retrofit first policy.
The what, how, why and when of deposit return schemes
Circular economy steps for plastic bottles and cans in England and Northern Ireland draws.
Join forces and share Building Safety knowledge in 2025
Why and how to contribute to the Building Safety Wiki.
Reporting on Payment Practices and Performance Regs
Approved amendment coming into effect 1 March 2025.